Introduction
It can be safely said that when one lists every available CMS being used on the web, Drupal stands out as the most secure framework. One major factor contributing towards this assessment is that Drupal security issues have always been a major concern for the team behind Drupal—the Drupal codebase was built from the ground up to account for security loopholes. Further, as Drupal has grown over the years, security has always remained a core focus area for Drupal maintainers.
The icing on the cake is the team of Drupal contributors who routinely monitor both the Drupal core as well as community contributed Drupal security modules. When potential loopholes are uncovered, they issue public service announcements (PSAs) which help the community and user base know that there might be security issues which are going to be fixed. There’s a process that the security team uses in their role, and you can find out more about how they work here. You can also view all PSAs issued by them here, and you can even reach out to the security team.
But at the end of the day, every site owner should keep Drupal security best practices in mind, and work towards implementing them. Securing your site can be done in many ways, and we’ve tried to dive into some of them in this post.
Writing Secure Code
One of the myriad advantages with Drupal is the ability to easily extend its core functionality by writing custom code. But, as Uncle Ben once said, “With great power comes great responsibility”—similarly, the fact that you can write custom code also means that you can inadvertently introduce security loopholes. They probably won’t affect the entire Drupal codebase and community, but they will certainly affect your site.
To that end, you can follow certain guidelines to make sure any custom code you write doesn’t end up breaking your site. For one, you can use Twig templates which automatically sanitize output to make sure cross-site scripting attacks aren’t possible. You could also use the database abstraction layer and inject variables and placeholder values into them. For instance, don’t do this:
| db_query('SELECT name FROM products p WHERE p.name = '. $_GET['product']); |
Doing this opens up your site to all kinds of SQL injection attack vectors. Instead, you can use argument substitution with db_query, and do this:
| db_query("SELECT name FROM products p WHERE p.name = :name", [':name' => $_GET['product']]); |
You can look up Drupal’s detailed guidelines on writing secure code here.
One of the fastest ways to do this is to introduce CI in your development workflow and use tools like Code sniffer and PHPCS with the help of Coder module. This can be done in local alone too if tools like Jenkins or Travis are not available or an overhead.
Drupal Security Updates
The key behind effective Drupal security policies is to make sure your site is always updated—both the Drupal core as well as third-party modules. The best way to find out if any updates are available for your site is to check your dashboard, and to keep track of Drupal’s PSAs.
It’s always a good idea to read up on a security update when it’s released to understand what issue(s) it fixes, and how it can affect your site as a whole. Sometimes, Drupal security updates may need additional site or database configuration/tinkering, and those details can be found in the update’s documentation.
Admin Interface
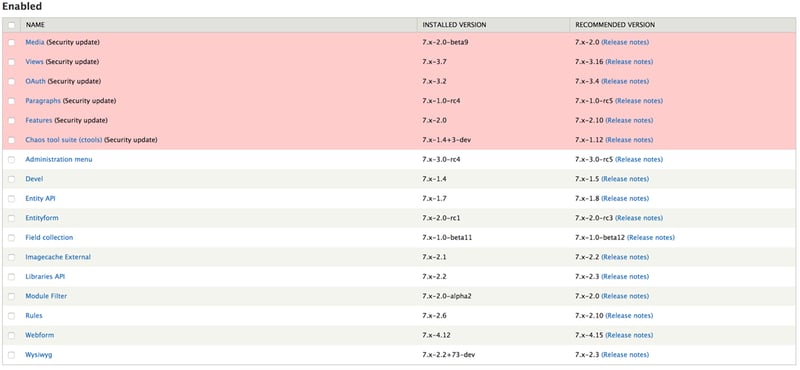
You can easily update Drupal modules and themes using the admin interface, unlike the Drupal core, which is updated through a terminal.
- First, you should enable the Update Manager module.
- Next, navigate to /admin/reports/status. If no updates are visible on the page, click “Check Manually”, under the Update row.
- If updates are detected, click on the “Available Updates” link, which will take you to a page showing a list of modules that have available updates.
- Now you need to select the modules you’d like to update, and click “Download these updates”. Before doing this, it’s a good idea to take a backup of your Drupal database, should things go south.
Drush
If you’re comfortable with using a terminal, then drush is going to be your Swiss knife when it comes to managing Drupal security updates. It’s a powerful command-line tool that makes the Drupal update process a lot easier with some simple commands. Before using drush, it’s recommended that you take a backup of both your site and your database.
- drush pm-updatecode OR drush upc → This updates the Drupal core as well as contributed projects to the latest recommended release.
- drush pm-updatecode --no-core --security-only → This command installs security updates for all third-party modules on your Drupal site.
- drush pm-updatecode --security-only → This command is handy for the day you feel like installing security updates for your entire site.
- drush pm-updatestatus/drush ups → You can use this command to show the status of security updates for all modules installed on your Drupal site.
- drush pm-updatecode <module1_name> <module2_name> … → This command can be used to update individual Drupal modules.
- drush updb → This command is used for installing database updates, and is usually used after all security updates have been installed.
- drush pm-update → This command installs updates and performs database updates and migrations.
- drush pm-update --security-only → This command is like drush pm-update, except that it only installs security updates.
Check here for more details.
Note: One should run updb after running pm-updatecode to ensure all code in update hooks of updated modules is executed.
Conclusion
Installing Drupal security updates can seem like grunt work at times, but the necessity of performing this task can never be overstated. An interesting and effortless way to automate Drupal security updates is to set up scheduled cron jobs to update your core and modules using drush, which frees you up from worrying about updates and manually performing them.
The best Drupal security processes and frameworks in the world won’t help much if site owners don’t track updates to their site, and install them when needed. With this guide, you should be able to understand how Drupal’s security team identifies potential security threats and notifies the community; you should also be able to put a framework in place for managing updates to your Drupal site.

Mitesh Patel, Technical Architect
Off work, Mitesh prefers to be next to his wife watching the latest sci-fi flick, or laughing at his own (incredibly dry) jokes.

 We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.


Leave us a comment