The most impactful customer experiences are data-driven. CDPs help organizations collect, unify, manage, and analyze customer data. This allows businesses to understand their customers better and deliver personalized digital experiences.
But selecting and implementing a CDP is not a straightforward journey. It’s a digital transformation that begins with organizations understanding what a CDP can do for them and how they can utilize the platform to their advantage.
Evaluating If You Need A CDP
Every organization likes to think they know their customers, but most are missing out. According to a study conducted by Mapp, an international provider of insight-led customer engagement, lack of customer insight is the biggest challenge in providing personalized experiences.
Successfully implementing a CDP can help fix this challenge. Submit this form to find out if your organization needs a CDP.
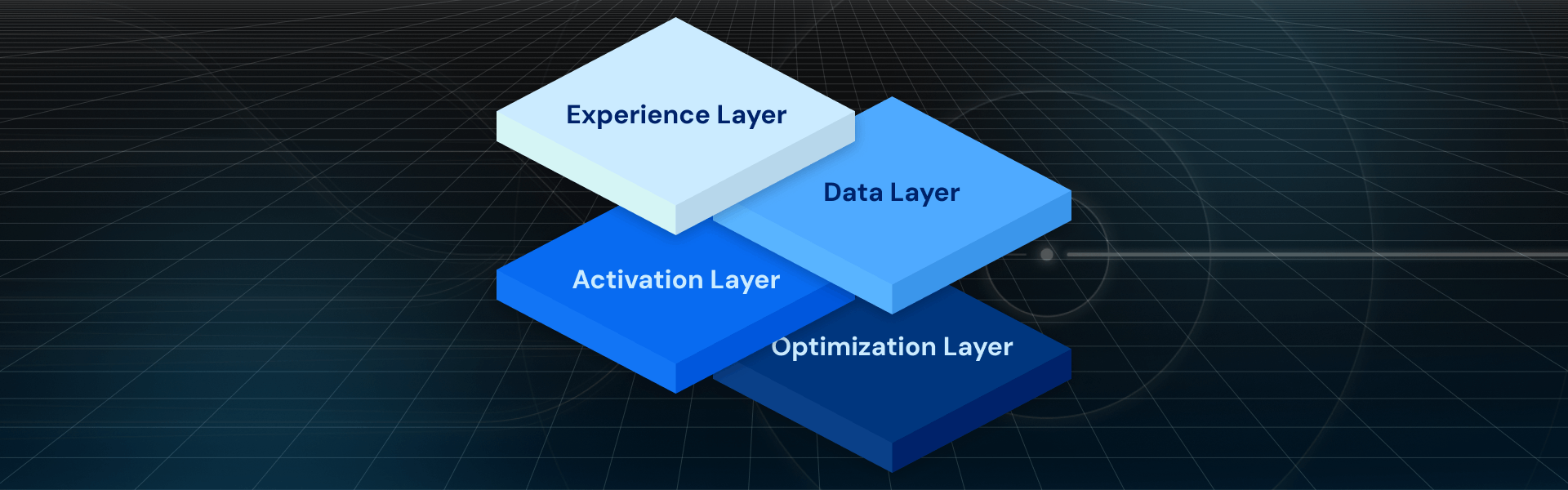
The CDP Implementation Framework: Everything From Discovery To Implementation & Enablement
Implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP) involves a structured approach encompassing discovery, strategy, implementation, and enablement.
Stage 1: Discovery
During the discovery phase, it's essential to gain a clear understanding of your organization's data landscape, business goals, and available resources. Key aspects include:
1. Data Maturity And Business Goals
To assess data maturity, consider the following:
- Volume: How much data does your organization generate and collect?
- Variety: What types of data are available (e.g., customer demographics, transaction history)?
- Velocity: How quickly is data generated and updated?
- Veracity: How reliable and accurate is the data?
- Value: What insights can be derived from the data to drive business decisions?
For example, a retail company may have vast amounts of transaction data but lack comprehensive customer profiles.
2. Data Inventory And Quality Assessment
Cataloging existing data sources involves identifying where data resides, such as:
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems
- Web analytics platforms
Assessing data quality entails evaluating data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. For instance, organizations may discover inconsistencies in customer information across different databases, impacting marketing campaigns' effectiveness.
3. Stakeholder Engagement And Workflow
Engage stakeholders from various departments (e.g., marketing, sales, IT) to understand their data needs and ensure alignment with business objectives. Establish clear roles and responsibilities, such as:
- Data stewards responsible for data governance
- Analysts tasked with generating insights from customer data
Define workflows to streamline data collection, processing, and analysis. For example, establish protocols for updating customer profiles and sharing insights across teams.
Key Questions To Ask
Ask relevant questions to guide the discovery process.
Project & Business Objectives
- What are the specific goals for this CDP implementation?
- What problem are you trying to solve with the CDP?
- What are your business goals and how does the CDP align with them?
- What would be considered a success for the CDP implementation?
- What are the current solutions and how can CDP improve them?
Budget & Timelines
- What is the budget for the CDP implementation?
- Is there a fixed deadline or time constraints for the project?
- Are there any financial limitations that need to be considered?
Identify Stakeholders
- Who are the primary stakeholders in this CDP project?
- What are the needs and expectations of each stakeholder?
- How will different stakeholders be involved in the project?
Data Sources & Quality
- What are the sources of your customer data?
- What is the quality and maturity of the data you currently have?
- Who owns the data and where does it come from?
Segmentation & Identification Strategy
- How will you segment your customer data?
- What is your strategy for identifying and resolving customer identities?
The Action Plan & Expectations
- What are the most impactful outcomes you expect from the CDP?
- How do you plan to monitor, measure, and capture the value of the CDP?
Ensure answers to all of these questions to develop an effective CDP implementation strategy.
Stage 2: Strategy
The strategy phase focuses on developing a comprehensive plan to leverage the CDP effectively. Key considerations include:
1. Data Strategy Development
Define a data strategy aligned with business objectives and use cases. For example:
- Personalization: Use customer data to deliver personalized experiences and targeted marketing campaigns.
- Customer Retention: Identify at-risk customers and implement strategies to improve retention rates.
Plan implementation phases in a "crawl, walk, run" approach to prioritize high-impact use cases and ensure gradual adoption across the organization.
2. Customer Data Landscape Assessment
Assess the customer data landscape by identifying all data sources and their integration capabilities. Consider:
- Online & Offline Data: Integrate data from online sources (e.g., website interactions, social media) and offline sources (e.g., in-store purchases, call center interactions).
- Identity Resolution: Develop a strategy for resolving customer identities across different data sources to create unified customer profiles.
Define the universal data layer, including data points and naming conventions, to ensure consistency in data collection and storage.
3. Stakeholder Engagement & Collaboration
Ensure alignment across departments and stakeholders by:
- Hosting workshops and collaborative sessions to gather input from various teams.
- Establishing a governance structure to manage data access, usage, and privacy.
- Define workflows and data ownership responsibilities to streamline collaboration and decision-making processes.
Stage 3: Implementation
During the implementation phase, the focus shifts to executing the plan and mapping data to the CDP effectively. Key steps include:
1. Data Mapping & Integration
Map data from various sources to the CDP to create a unified view of customer data. For example:
- Integrate CRM data to track customer interactions and purchase history.
- Combine website analytics data to understand customer behavior and preferences.
- Implement identity resolution to merge duplicate customer records and create accurate customer profiles.
2. Identity Resolution
An important part of data implementation is identity resolution (IR). When there's a surge of customer data coming in from various channels, it can be quite challenging to filter through everything. An easy solution is if you have a Customer Data Platform (CDP).
Imagine records like this:
|
Draco Malfoy |
Draco |
D. Malfoy |
|
[ ] |
Malfoy Manor |
[ ] |
|
[ ] |
[ ] |
Wiltshire, England |
|
dmalfoy@hunter.com |
[ ] |
[ ] |
These three records are of the same person only. But more basic systems might mix the data up and create three separate Dracos. A CDP will use its IR powers to consolidate an example like this into a single customer profile. The resolved record would complete Mr. Malfoy’s profile.
|
Draco Malfoy Malfoy Manor Wiltshire, England dmalfoy@hunter.com |
Stage 4: Enablement
The enablement phase involves preparing for operational deployment and deriving value from the CDP. Key activities include:
1. Provisioning & Training
Set up the production environment and train users on CDP functionalities, including:
- Data ingestion and integration processes
- Segmentation and targeting capabilities
- Reporting and analytics features
Build segments, reports, and personalized campaigns to leverage customer data effectively in marketing initiatives.
2. Iteration & Scaling
Start with small, manageable goals for quick wins and iterate based on feedback and insights from the CDP. For example, test different segmentation strategies to identify high-value customer segments.
Users can also analyze campaign performance metrics to optimize targeting and messaging. Scale up over time by expanding the use of the CDP across departments and incorporating additional data sources and use cases.
Conclusion
Do you need more help in building a strategic roadmap for a CDP implementation? Or are you not even sure if opting for a CDP is the right solution?
Submit the form to get personalized recommendations from our CDP experts.

Abhishek Dhariwal, Senior DXP Consultant
Abhishek is a true explorer—whether it’s different cuisines, places, or subjects, he enjoys it all. He reads at least two newspapers daily, values attention to detail, and prioritizes thoughtful solutions over quick fixes. Away from work, you can find this technophile enjoying TV Series.

Simran Sethi, Marketing Associate
Simran is an avid reader. She is an active runner, who also likes to swim, dance, and sing. For her, the meaning of life lies in the little things. Kindness, passion, and compassion are her life’s essential values.

 We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.


Leave us a comment